Gluten/wheat sensitivity

Practical guide for diagnosing gluten / wheat sensitivity
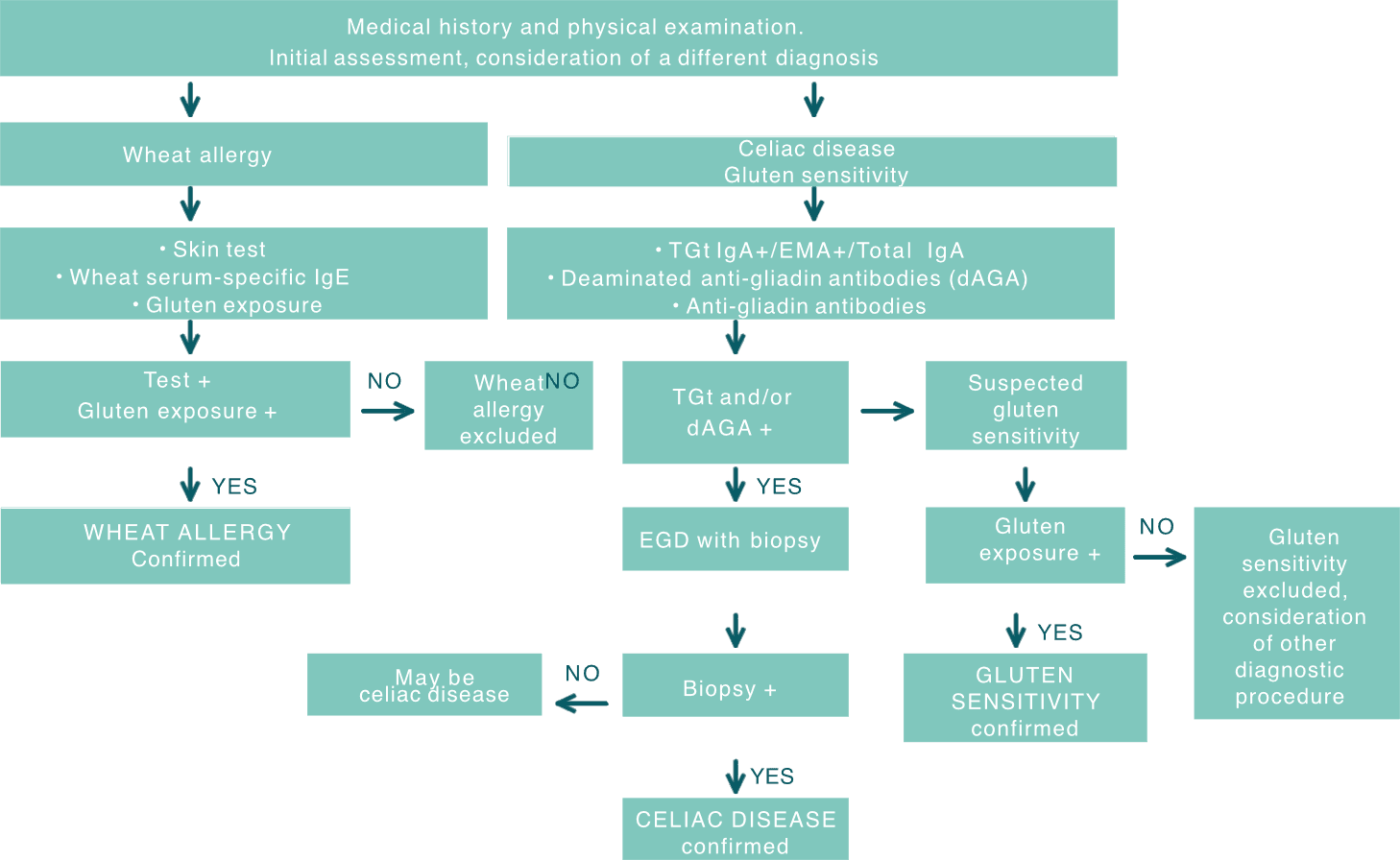
On the way to a diagnosis of gluten / wheat sensitivity, after ruling out coeliac disease and wheat allergy, it should be investigated whether a gluten-free diet improves symptoms. There are no specific bio-markers for a gluten sensitivity test / wheat sensitivity.
Who should be tested for gluten / wheat sensitivity?
If patients complain of non-specific symptoms such as abdominal pain, headaches or fatigue after eating gluten-containing foods, they may have a gluten / wheat sensitivity (Non Celiac Gluten Sensitivity, NCGS or Non Celiac Wheat Sensitivity, NCWS). Due to the symptomatic overlap phenomenon cereal- and gluten-related diseases(GRD) , a comprehensive clinical and laboratory examination is initially required in such cases to rule out coeliac disease and subsequently also wheat allergy. Once these two diseases have been reliably ruled out, the actual NCGS / NCWS diagnosis can begin.
Step by step to the diagnosis of gluten / wheat sensitivity
The first step on the way to a gluten / wheat sensitivity diagnosis is a careful assessment of the initial symptoms. It is important that the patient is still eating a normal diet - i.e. one containing gluten - at this point in time andhas been doing so for at least six weeks. There are currently no specific biochemical, immunological or histopathological markers associated with gluten / wheat sensitivity. In the second step, a gluten-free diet should be prescribed for at least six weeks. Following the gluten-free diet phase, the symptoms should be monitored. If there is an improvement in symptoms, for final validation of a diagnosis of gluten/ wheat sensitivity, a return of symptoms following a dietary re-challenge with gluten should be observed.
The steps of gluten / wheat sensitivity Diagnostics:
- Exclusion of coeliac disease and wheat allergy
- Determination of the initial symptoms under a gluten-containing diet
- Gluten-free diet for at least six weeks
- Medical assessment of the prevailing symptoms
- Gluten re-challenge to confirm the diagnosis of gluten / wheat sensitivity
Gluten re-challengeto confirm the diagnosis of gluten / wheat sensitivity
If gluten / wheat sensitivity is present, the symptoms usually reduce within a few days to two weeks if the affected person eats a gluten-free diet. However, the diagnosis of gluten / wheat sensitivity is not only confirmed by the improvement or disappearance of symptoms on a gluten-free diet - but also by a renewed deterioration as soon as gluten is consumed again. In order to confirm the diagnosis of gluten / wheat sensitivity in people who respond to a gluten-free diet, a provocation using gluten-containing foods is therefore necessary.
What if it is not a gluten / wheat sensitivity?
If coeliac disease, wheat allergy and gluten / wheat sensitivity have been ruled out as the cause of the cereal or gluten-related symptoms, the presence of irritable bowel syndrome can also be clarified diagnostically.
This might also interest you

How to successfully diagnose coeliac disease in practice
Read moreSources
- Al-Toma A et al. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United European Gastroenterol J. 2019 Jun;7(5):583-613.
- Felber J et al. Updated S2k guideline coeliac disease of the German Society for Gastroenterology, Digestive and Metabolic Diseases (DGVS), Z Gastroenterol 2022; 60: 790-856.
